What is Literacy Rate?
Literacy rate refers to the percentage of literate people among persons aged seven and above. According to the Census 2011, a person is referred as literate when they can read and write with understanding in at least any one language. According to the National Literacy Mission Programme, a person must attain the skills of reading, writing and arithmetic to be entitled as literate. The person must have basic comprehension skills to communicate efficiently and solve day-to-day problems also determines literacy. The government of India has taken various measures to improve literacy rates in India.
Current Status of Literacy rate in India : Data from Census 2011
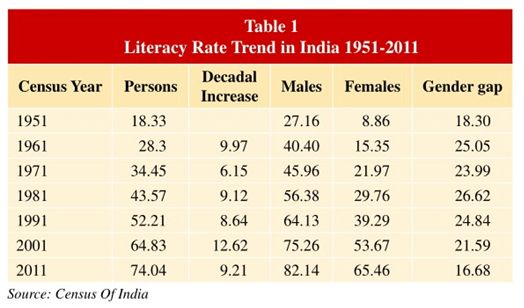
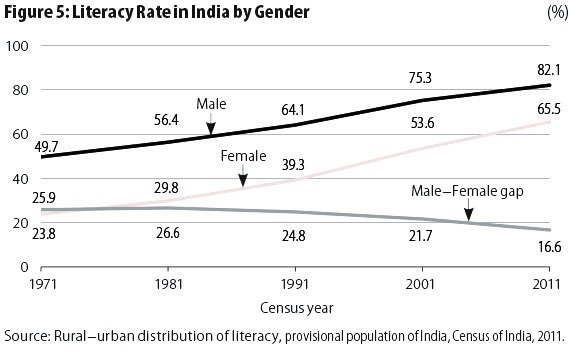
- As per census 2011, literacy rate in India is 74.04%. the corresponding literacy rates for male and female are 82.14% and 65.46% respectively.
- Improvement in Literacy rates when compared with 2001
- Overall improvement – 9.21%
- Improvement of literacy rate in male – 6.88%
- Improvement of literacy rate in female – 11.79%
- According to 2011 Census, literacy rate in urban areas was greater 87.7% than rural areas with 73.5%.
Report On Literacy Rate in India
The report on ‘Household Social Consumption: Education in India as part of 75th round of National Sample Survey – from July 2017 to June 2018’ has been released just before the International Literacy Day (8th September). It is based on the National Statistical Office (NSO) survey and provides state-wise detail of literacy rate among the persons aged seven years and above.
Key Findings Of The Report
- Overall literacy rate of India is 77.7% with 87.7% in urban areas and 73.5% in rural areas.
- The literacy rate of males is 84.7% and of females is 70.3% in India. The male literacy rate is greater than the female literacy rate among all states with a considerable gap in the worst-performing states.
- The best performers are Kerala>Delhi>Uttarakhand>Himachal Pradesh>Assam.
- The worst performers are Andhra Pradesh < Rajasthan < Bihar < Telangana < Uttar Pradesh.
- Digital Literacy:
- 23% of urban households and 4% of rural households have computers.
- Persons in the age group of 15-29 years, nearly 56% in urban areas and 24% in rural areas can operate computer.
- In the same age group, nearly 25% in rural areas and 58% in urban areas know how to use the internet.
Major Causes Of Illiteracy
- Poverty: Due to poverty poor people cannot afford basic livelihood can often lead to Illiteracy. Instead of admitting their children in schools’ families with low income prefer that their children start working at a young age.
- Lack of Awareness: The lack of awareness about the significance of education is also plays the major role in increasing illiteracy rate. In remote rural areas, illiteracy rates are much higher because many people never had any formal education.
- Lack of Infrastructure: There are certain remote and rural areas in which schools are not present so parents hesitate to admit their children in a school which is far from their home. Also, there are transportation facilities available, but most of the families cannot afford it.
- Uneducated Parents: Children of uneducated parents who neither read nor write are more likely to stay uneducated. Parents who had some formal education understand the significance of education and its role in shaping a bright future for their children.
Government Initiatives towards increasing Literacy rate
- Education and Literacy Programmes
- National Education Policy, 2020: It aims to achieve 100% youth and adult literacy and make “India a global knowledge superpower” by introducing several reforms from the school to college education in the Indian education system.
- Midday Meal Scheme: The scheme provides meals for all school going children in Classes I-VIII of Government, Government-Aided Schools.
- Samagra Shiksha:It is an integrated scheme for school education extending from pre-school to class XII to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education. It subsumes the three Schemes: Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA), Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA) and Teacher Education (TE).
- Right to Education: Under Article 21-A, the Right to Education Act (RTE) provides free and compulsory education for children as a basic right.
- Digital Literacy Programmes
- Digital India Programme: Digital India is an umbrella scheme of government of India with an aim to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledgable economy.
- Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan: It is one of the initiatives by the government to make indian citizens digitally literate.
- National Digital Literacy Mission: This mission is launched with the objective to empower at least one person per household with essential digital literacy skills by 2020.
- Bharat Net Programme: It is the project by government of India which aims to digitally connect all the villages and gram panchayats of India.

